首页 > 离子通道阅读器
Aurora的离子通道阅读器(ICR)结合多功能性、精密度和灵敏度与微进样工艺和液体处理技术,为离子通道研究人员创造了高通量的筛选解决方案,填补了自动化膜片钳无法填补的空白。
ICR技术对带电及电中性的通道和转运蛋白都有很高的灵敏度。ICR 12000的惊人的每天60000个样本的通量使离子通道研究人员能够在药物发现过程的早期获得化合物QT的可靠性,提供了在药物发现过程早期获得化合物的能力。
目前的应用包括阳离子氯共转运蛋白(CCC)的评估,CCC是神经元氯稳态的关键组成部分,是细胞体积和神经元兴奋性的重要调节因子。因为CCC是电中性的,它们的活性不能用自动膜片钳技术来测量。离子通道阅读器能够通过测量细胞溶质和细胞外离子的绝对浓度来获得这些和其他通道及转运蛋白的高通量活性测量,这一技术独立于依赖于电压操纵的方法,并且是对这些方法的补充。
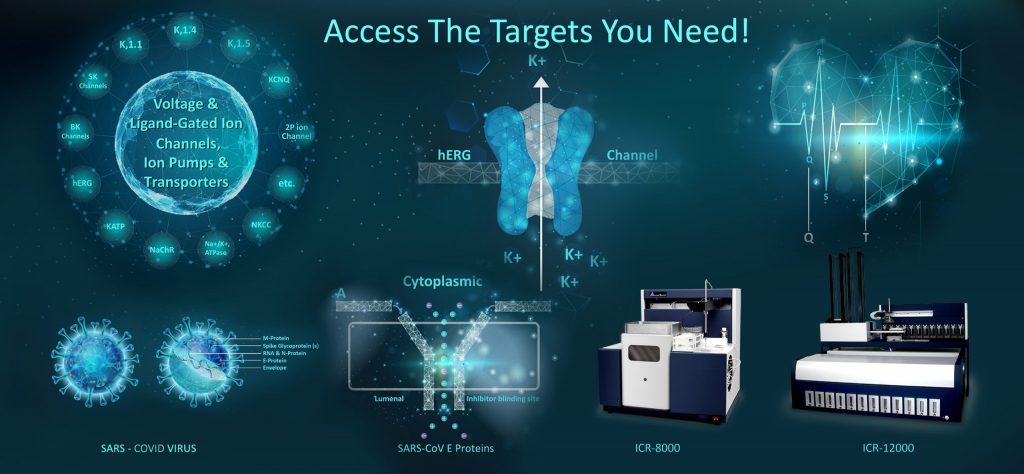
人类基因组测序确定了400多个据称的离子通道和转运体。这些膜蛋白的功能测试数量有限。离子通道和转运体的广泛组织分布及其生理功能使这些蛋白质成为药物发现、开发和安全性的重要治疗靶点。此外,这些膜蛋白在不同类型的人类癌症中表达,代表了新的癌症生物标志物。离子通道也在新型SARS-CoV-2病毒及其宿主细胞膜上表达,被认为是2019冠状病毒疾病潜在的药物和疫苗开发靶点。随着离子通道筛选新技术的出现,我们的知识显著增强。Aurora Biomed的离子通道阅读器(ICR)将元素分析的多功能性、精密度和灵敏度与微采样过程和液体处理技术相结合,为离子通道研究人员创造了一种中高通量筛选解决方案,填补了自动化膜片钳无法填补的空白。
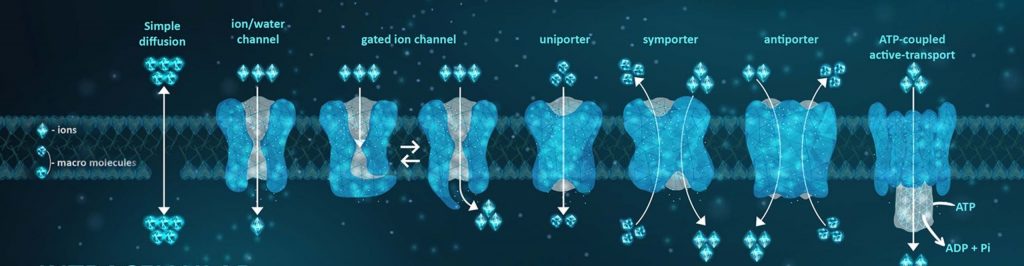
Aurora的ICR系列是通过检测细胞内外离子浓度来量化检测离子通道的离子运动的。这是一种独立于依赖于电压操纵的方法,并与之互补的技术。由于离子通量是通道和转运体活性的直接测量方法,因此此类分析方法稳健且对干扰不太敏感。ICR系列产生的数据非常一致,可以预测药物效力。
Aurora目前正在与制药和学术合作伙伴合作,开发新的、有效的基于ICR的分析方法,用于转运体、天然产物、癌症生物标记物以及药物发现研究。
离子通道功能故障与囊肿性纤维化,糖尿病,男性阳痿,癫痫病,心力衰竭,高血压,肌肉硬化,肥胖症,精神分裂症,和镰状细胞性贫血等疾病与失调是有关联的。
离子通道阅读器可用于评估电压门控(hERG、BK/SK、Kv1.1、1.4、1.5、KCNQ、2P等)和配体门控(KATP、nAChR等)离子通道,以及离子泵和转运体(如Na+/K+-ATP酶),使研究人员能够加速药物开发,用于治疗和预防与这些关键膜转运蛋白相关的疾病。
目前的应用包括阳离子氯共转运蛋白(CCC)的评估,CCC是神经元氯稳态的关键组成部分,是细胞体积和神经元兴奋性的重要调节因子。因为CCC是电中性的,它们的活性不能用自动膜片钳技术来测量。离子通道阅读器能够通过测量细胞溶质和细胞外离子的绝对浓度来获得这些和其他通道及转运蛋白的高通量活性测量,这一技术独立于依赖于电压操纵的方法,并且是对这些方法的补充。
Aurora的离子通道阅读器(ICR 8000和ICR 12000)被用作促进任何离子通道/转运体研究或筛选的工具,其中离子运动的测量提供了对通道活动的有意义的见解。鉴于ICR的自动化工作流程和高通量,大型制药公司尤其青睐ICR。学术机构发现,这项技术以较低的运营成本提供了合理的数据输出。

ICR 12000设计用于化合物库的超高通量离子通道筛选,包括多通道采样和增强的自动化功能。基于Aurora Biomed原子吸收的多功能性、精密度和灵敏度,ICR 12000适用于使用基于细胞的通量分析的配体门控和电压门控离子通道。
ICR 12000——高通量药物筛选技术
ICR 12000设计用于化合物库的超高通量离子通道筛选,包括多通道采样和增强的自动化功能。基于Aurora Biomed的元素分析仪器的多功能性、精密度和灵敏度,ICR 12000适用于使用基于细胞的通量分析的配体门控和电压门控离子通道。凭借Aurora Biomed的ICR技术的稳健性,该阅读器为电致和电中性通道及转运体提供了高灵敏度。ICR 12000每天处理60000个样本,这让离子通道研究人员能够在药物发现过程的早期获取化合物QT。

ICR8100是一种更经济实惠的、中等吞吐量的离子通道筛选系统,对于台式机来说足够紧凑,同时保留了广泛的实用性。
ICR 8100中通量药物筛选技术
ICR 8100是一种中等吞吐量的离子通道筛查系统,是一种价格合理、灵敏度高的系统,在保持广泛实用性的同时,它足够紧凑,可用于台式机。ICR 8000可用于评估电压门控和配体门控离子通道,以及离子泵和转运体,使研究人员能够加速用于治疗和预防疾病的药物开发。可编程和自动化解决方案,每天可用于高达5000份样本。消除了与荧光相关的猝灭效应,消除了使用有害放射性同位素的需要。
Roche的研究人员利用ICR12000对阳离子氯化物共转运蛋白的调节剂进行了高通量筛选。
从2016年离子通道峰会上下载他们的海报,了解罗氏公司如何开发出一种高通量铷(Rb+)摄取测定法,用于测量NKCC1功能,并随后使用Aurora的ICR 12000筛选了120万种化合物。

非放射性铷通量测定法的建立,用于高通量筛选电中性NKCC1离子转运蛋白。
下载与罗氏公司合作研究的出版物,开发用于测量电中性NKCC1活性的高通量铷(Rb+)通量测定法。

ICR 8100和ICR 12000可应用在以下的离子通道研究:
• 电压门控性钾离子通道,包括hERG, Kv1.1, Kv1.4和Kv1.5
• 牵张激活钾离子通道
• 电压门控钠离子通道,包括NaV1.2, NaV1.5和NaV1.7
• 配体门控离子通道,包括GABAA, P2X, KATP, SKCa, BKCa 和 nAChR
• 运输载体,包括Na/K-ATPase 和K-Cl 共转运载体
Aurora公司的离子通道阅读器技术不仅可应用于在细胞水平表达的离子通道靶点,也可应用在合成小泡中表达的离子转运通道或者孔形成蛋白。

